10.4: The Ideal Gas Equation - Chemistry LibreTexts
4.5 (718) · $ 6.99 · In stock
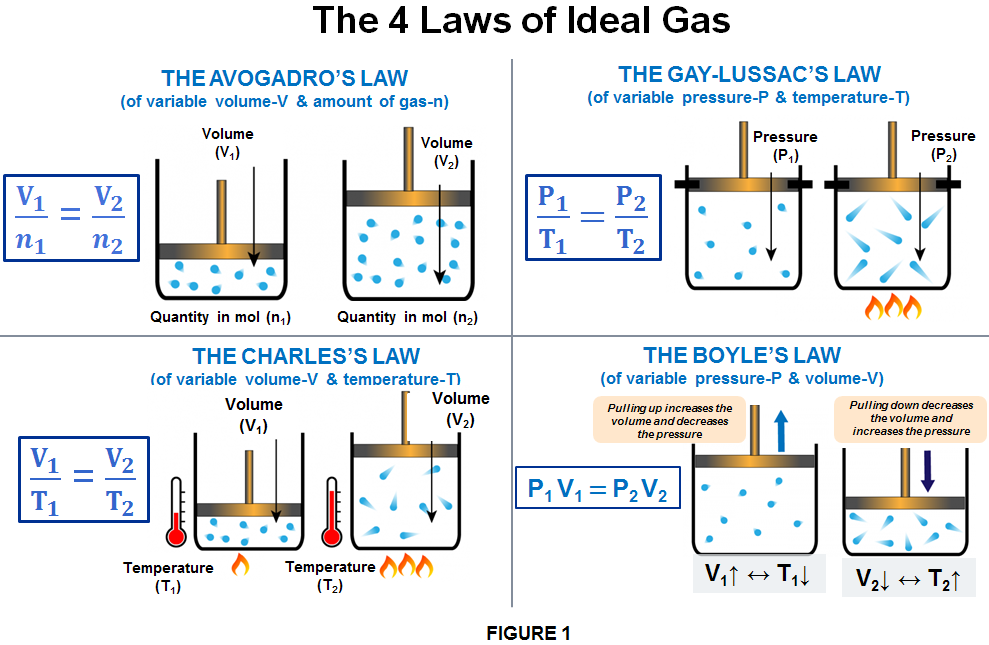
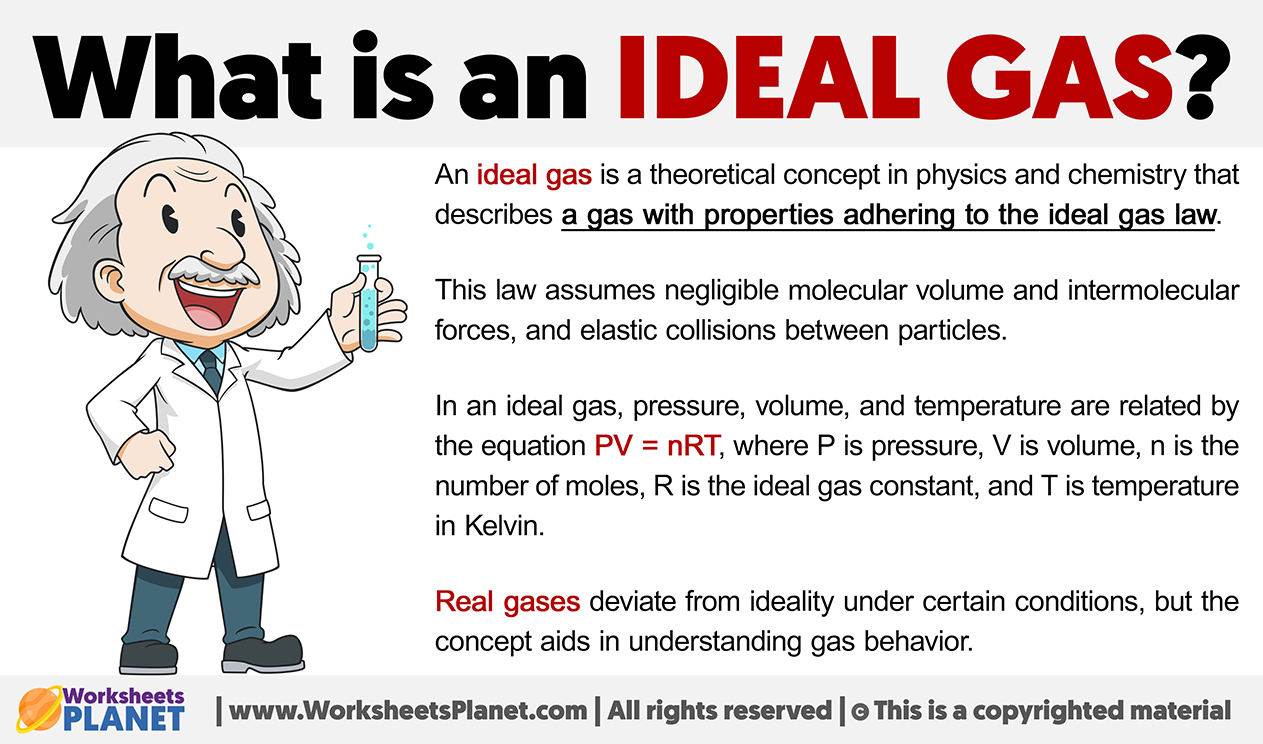
The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the …
The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the gas constant. The ideal gas law describes the behavior of an ideal gas, a hypothetical substance whose behavior can be explained quantitatively by the ideal gas law and the kinetic molecular theory of gases. Standard temperature and pressure (STP) is 0°C and 1 atm.

9.8 Non-Ideal Gas Behavior – Chemistry Fundamentals

487928109-Physical-Chemistry-McQuarrie-and-Simon-Full.pdf
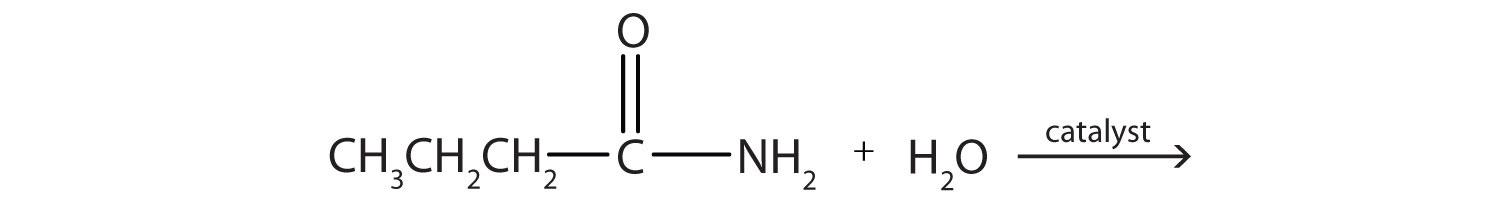
CH105: Chapter 10 - Compounds with Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Nitrogen - Chemistry

14.5 Equilibrium and Thermodynamics – Chemistry Fundamentals

Acid rain, Definition, Causes, Effects, & Formulas
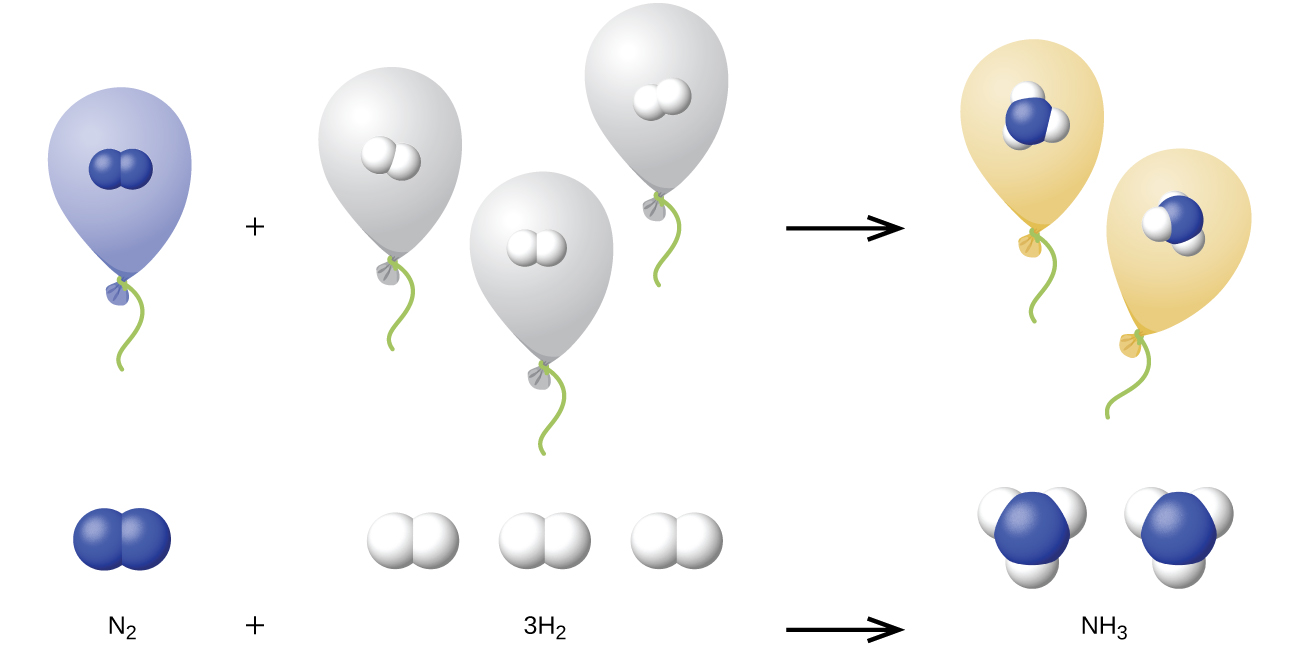
10.3: Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions - Chemistry LibreTexts

Foods, Free Full-Text

Chapter 10 Gases by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University 1 - ppt download

487928109-Physical-Chemistry-McQuarrie-and-Simon-Full.pdf
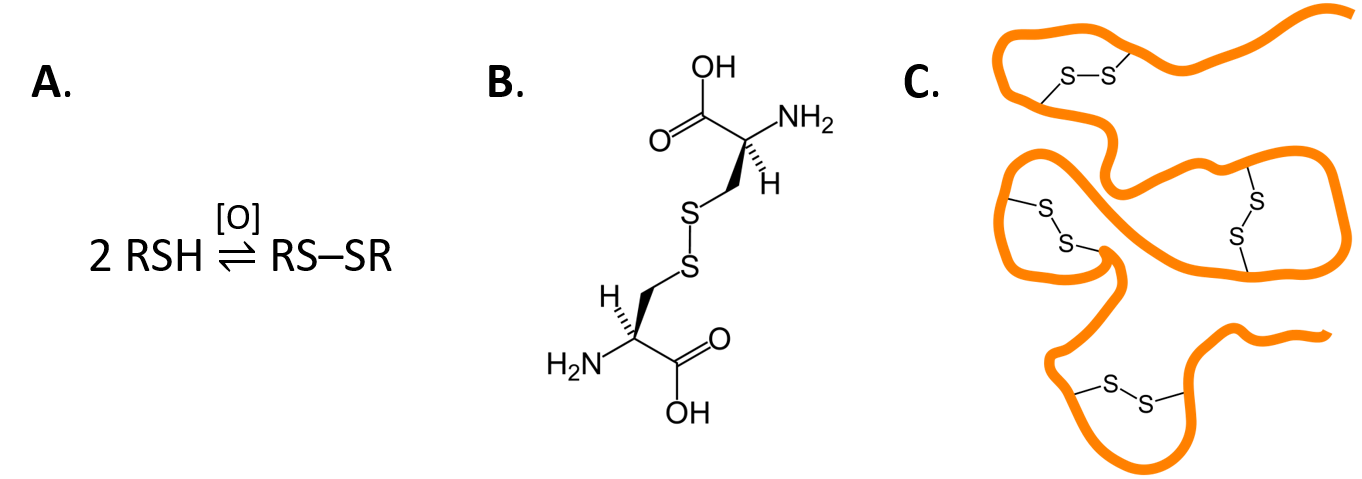
CH105: Chapter 10 - Compounds with Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Nitrogen - Chemistry
1. An unspecified ideal gas at 10°C and 100kPa occupies a volume of 2.5 m³. (a) How many moles does this gas have? (b) If the pressure and temperature are raised three

Eutectics: formation, properties, and applications - Chemical Society Reviews (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1CS00404B

TEST BANK chapter 5 - Test bank Chapter 5 gases 1. Which statement is false? a The density of a gas is constant as long as its temperature
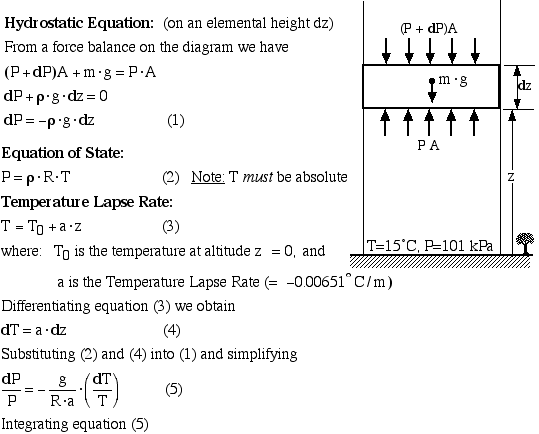
Chapter 2b: Pure Substances: Ideal Gas (updated 1/17/11)
Ideal Gas Law - Wyzant Lessons