Optical Coherence Tomography: Imaging Mouse Retinal Ganglion Cells In Vivo
4.8 (259) · $ 26.99 · In stock
Scientific Article | Structural changes in the retina are common manifestations of ophthalmic diseases.

Researching Review of Advances in Ophthalmic Optical Imaging Technologies from Several Mouse Retinal Imaging Methods

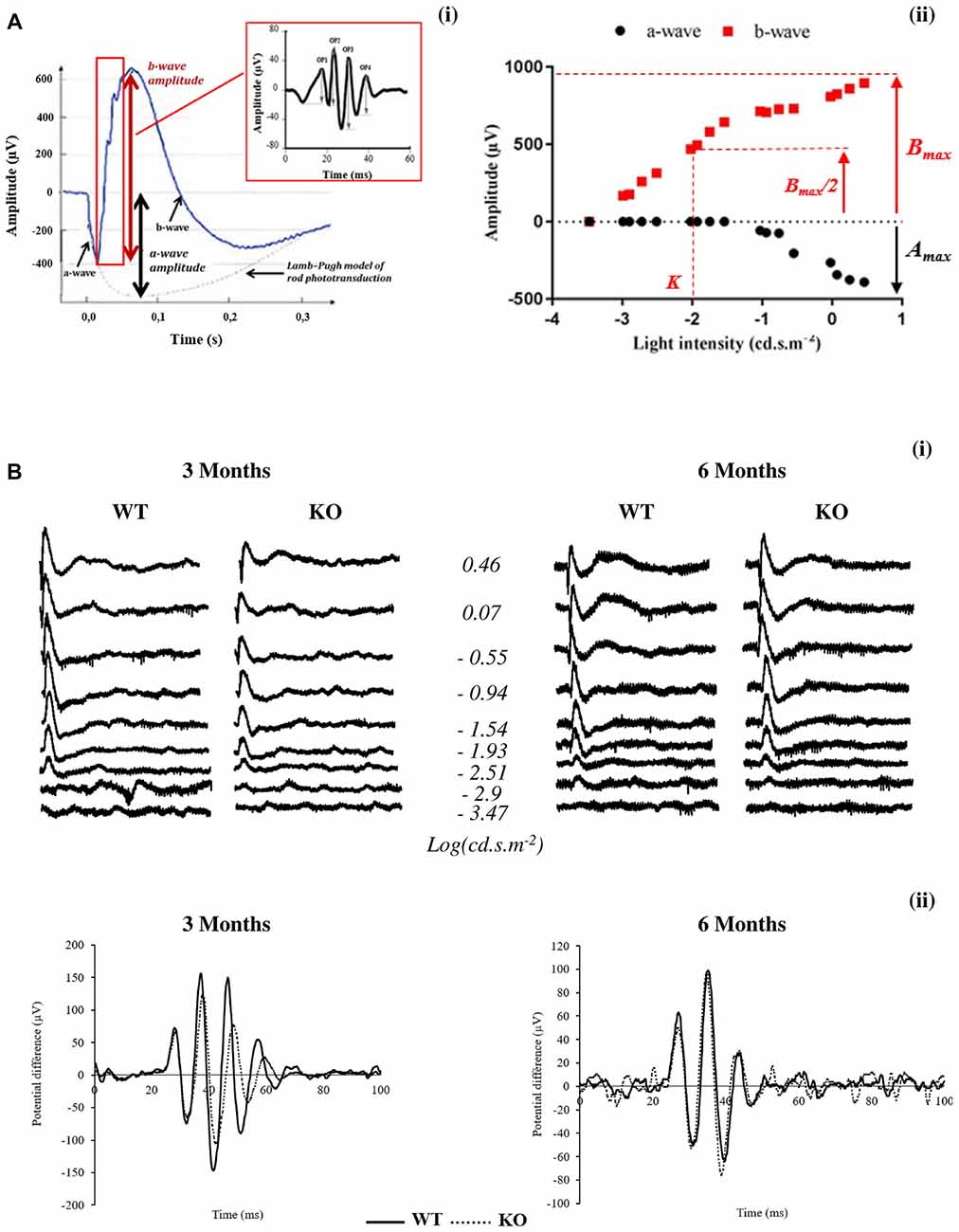
Topical Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) restores electrophysiological alterations in the Ins2Akita mouse model of diabetic retinopathy - ScienceDirect
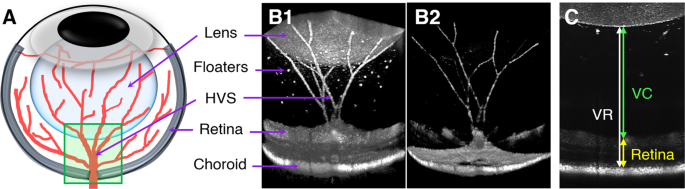
Longitudinal OCT and OCTA monitoring reveals accelerated

Monitoring retinal changes with optical coherence tomography predicts neuronal loss in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, Journal of Neuroinflammation
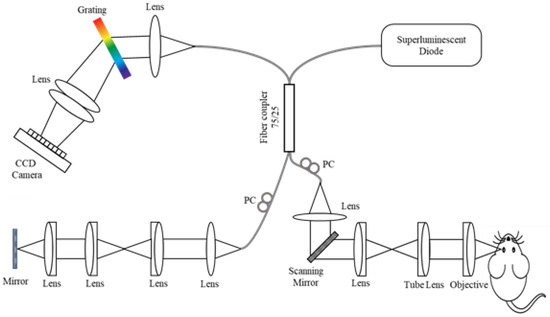
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
Frontiers Early Retinal Defects in Fmr1−/y Mice: Toward a Critical Role of Visual Dys-Sensitivity in the Fragile X Syndrome Phenotype?

PDF) Retinal Phenotyping of a Murine Model of Lafora Disease

In vivo imaging of adeno-associated viral vector labelled retinal ganglion cells
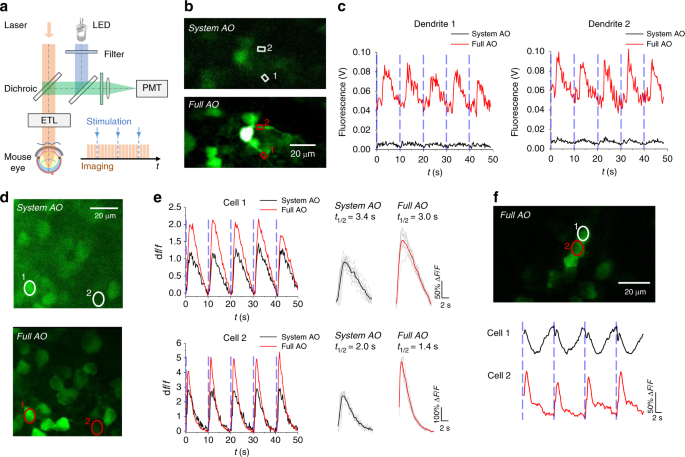
Adaptive optics two-photon microscopy enables near-diffraction-limited and functional retinal imaging in vivo
Adaptive-optics SLO imaging combined with widefield OCT and SLO enables precise 3D localization of fluorescent cells in the mouse retina

Human adipose tissue-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles attenuate ocular hypertension-induced retinal ganglion cell damage by inhibiting microglia- TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB proinflammatory cascade signaling, Acta Neuropathologica Communications

All Protocols and Video Articles in JoVE

Topical Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) restores electrophysiological alterations in the Ins2Akita mouse model of diabetic retinopathy - ScienceDirect







)




